# WINkLink 可验证随机数服务
# 概览
可验证随机函数(VRF)是公钥版密钥加密哈希,可作为随机数使用。 仅私钥持有者可进行哈希运算,但任何公钥持有者均可验证哈希运算结果是否正确。 VRF 可用于生成安全可靠的随机数。
随机数由 seed(由用户提供)、nonce(VRFCoordinator 合约的私有状态)、区块哈希(请求事件所在区块)和预言机节点的密钥决定。
VRF 的生成过程如下:
- Dapp 合约发出生成随机数的链上请求;
- 链下预言机节点监听到该请求后,将生成随机数并附上加密证明以供验证,随后将其回传至预言机合约(VRFCoordinator);
- 经预言机合约验证后,该随机数将通过回调函数发布至 Dapp 合约。
上述流程可确保预言机运营商、矿工、用户乃至智能合约开发人员等任何人都无法篡改或操纵随机数。
WINkLink VRF 是专为 Dapp 合约设计的公平、可验证的随机数生成来源。 Dapp 合约的开发者可将 WINkLink VRF 用作防篡改随机数生成器(RNG),为任何依赖随机数的应用程序创建可靠的智能合约,包括:
- 区块链游戏和 NFT
- 职责和资源的随机分配(例如随机分配法官审理案件)
- 选择具有代表性的共识机制样本
WINkLink VRF 解决方案由链上和链下两部分组成:
- VRF Coordinator(链上部分):可与 VRF 服务交互。 当发起随机数请求后,VRF Coordinator 将触发一个事件,并对VRF 服务生成的随机数和证明进行验证。
- VRF Wrapper(链上部分):对 VRF Coordinator 进行封装,为调用合约提供接口。
- VRF 服务(链下部分):通过订阅 VRF Coordinator 事件日志监听请求,并根据区块哈希和 nonce 计算随机数, 随后将包含随机数和随机数生成证明的交易发送至 VRFCoordinator。
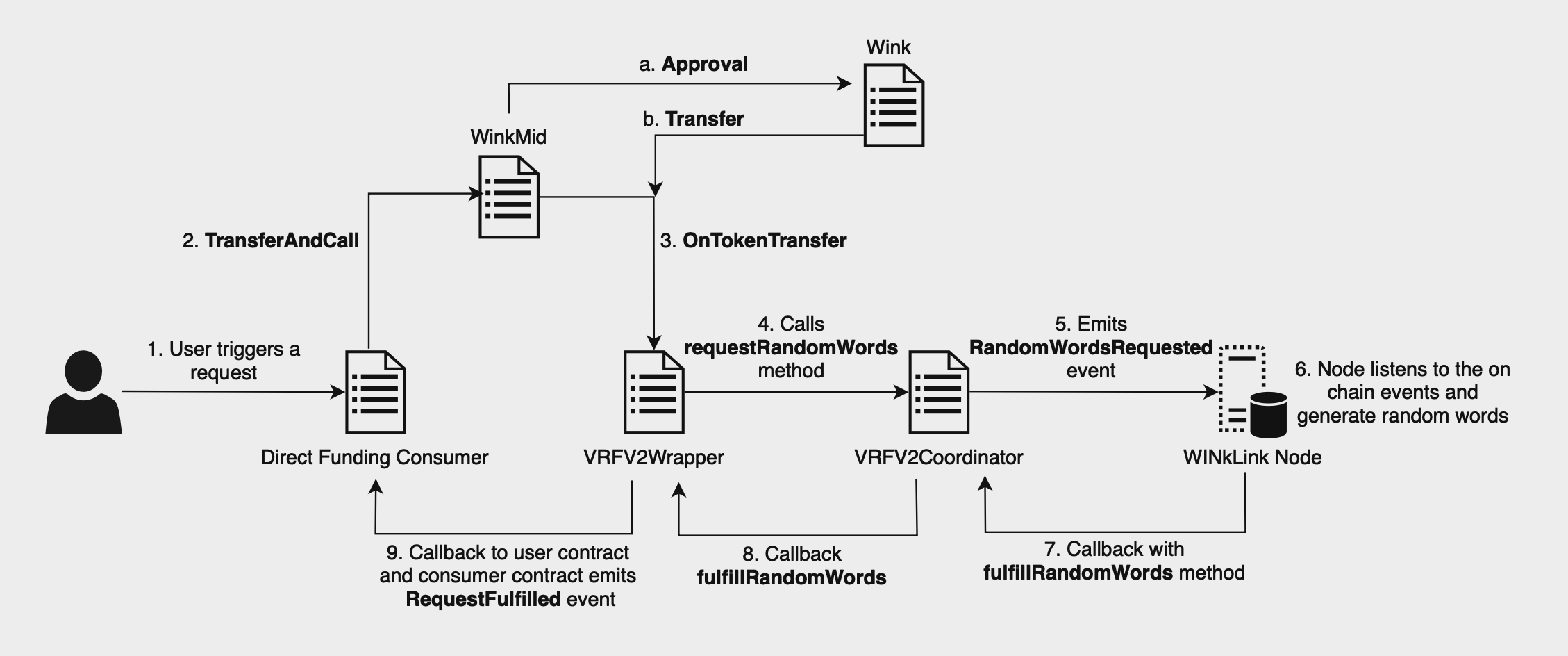
# 直接资金流
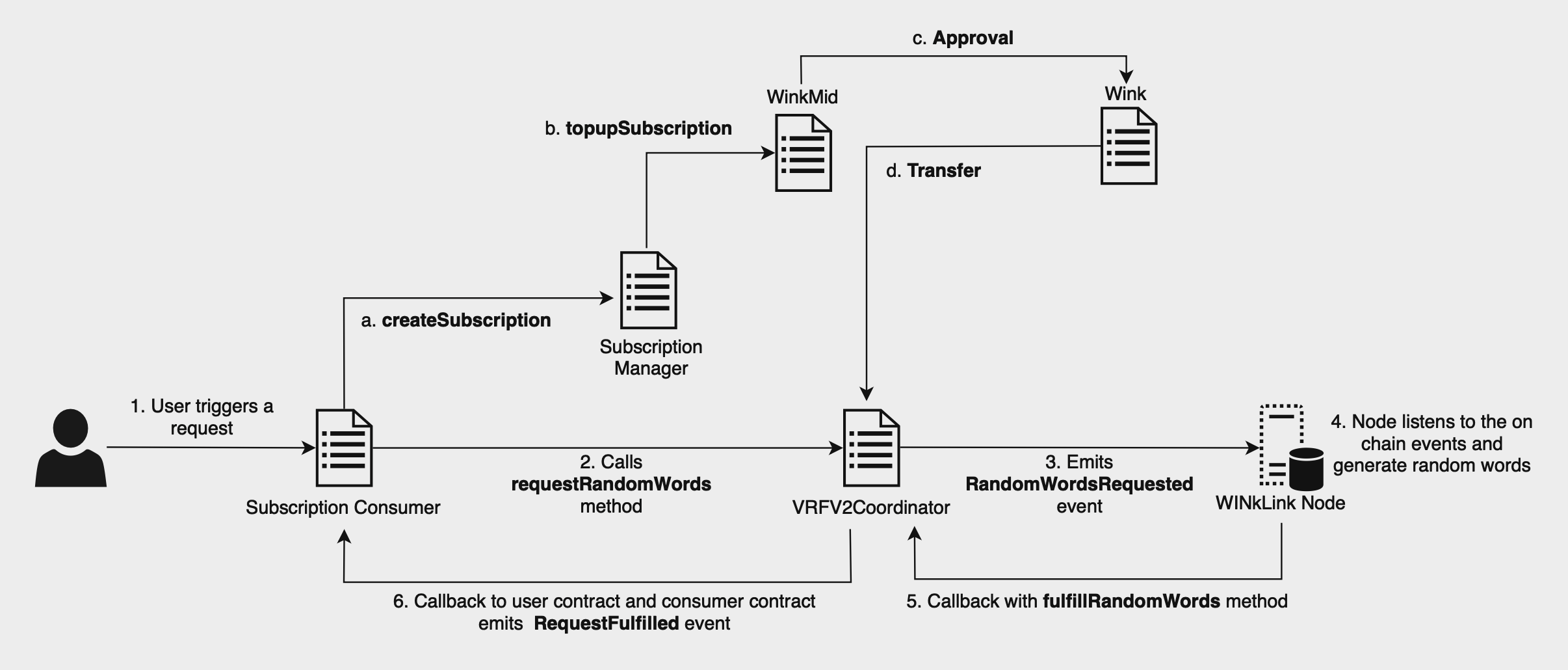
# 订阅流
# 波场 Nile VRF 合约
为方便开发者使用,Nile 测试网部署了 WinkMid 合约,并封装了 WIN 代币。 开发者可直接使用该合约地址,无需额外部署。 Nile 测试网还提供水龙头地址,可供用户领取 TRX 和 WIN 测试代币。
| 内容 | 值 |
|---|---|
| WIN Token | TNDSHKGBmgRx9mDYA9CnxPx55nu672yQw2 |
| WinkMid | TLLEKGqhH4MiN541BDaGpXD7MRkwG2mTro |
| BlockHashStore | TBpTbK9KQzagrN7eMKFr5QM2pgZf6FN7KA |
| VRFCoordinatorV2 | TDidecxMyGMgqvYS7nmpMQCZ16HqqV5Fke |
| VRFV2Wrapper | TMNRLGXhe3gzbUyWccuQAKhfVKFyqmLE1W |
| Fee | 10 WIN |
测试网水龙头地址: https://nileex.io/join/getJoinPage (opens new window)
# 波场主网 VRF 合约
| 内容 | 值 |
|---|---|
| WIN Token | TLa2f6VPqDgRE67v1736s7bJ8Ray5wYjU7 |
| WinkMid | TVMhaFMynYqTRLB1xShYL7wBwdmQHH6bKV |
| BlockHashStore | TRGmef4qUdNJ4xTEL96hToGuMTNst57aS1 |
| VRFCoordinatorV2 | TZCz1BcnYviUNDiLvG6ZeuC477YupDgDA7 |
| VRFV2Wrapper | TGDVwQRKwtNHrwy4RFG49b2HTHkvWckP5N |
| Fee | 10 WIN |
# 如何使用现有的 WINkLink 可验证随机数服务
# VRF 请求流程
Dapp 合约调用 VRFV2Wrapper 的 calculateRequestPrice 函数,估算生成随机数需要的交易成本。
Dapp 合约调用 WinkMid 的 transferAndCall 函数,向 Wrapper 支付计算出的请求价格。 此方法会发送 Wink 代币并执行 VRFV2Wrapper 的 onTokenTransfer 逻辑。
VRFV2Wrapper 的 onTokenTransfer 逻辑触发 VRFCoordinatorV2 的 requestRandomWords 函数,并请求随机数。
VRFCoordinatorV2 合约发布 RandomWordsRequested 事件。
VRF 节点捕获此事件并等待指定数量的区块确认, 随后通过 fulfillRandomWords 函数向 VRFCoordinatorV2 合约返回随机值及其证明。
VRFCoordinatorV2 合约在链上对证明进行验证,随即调用 VRFV2Wrapper 的 fulfillRandomWords 函数。
最后,VRFV2Wrapper 回调 Dapp 合约,完成请求。
# 准备事项
WINkLink 的维护者需要对波场 TRON 有一定的了解,且熟悉智能合约的部署和调用流程。 建议阅读波场相关的官方文档 ,特别是 TronIDE 上进行合约部署的相关文章。
准备节点账户。 建议阅读节点账户准备相关的文档。
# VRFCoordinatorV2 合约
VRFCoordinatorV2 合约部署在波场 TRON 公链上,拥有以下功能:
- 接收 Dapp 合约的随机数请求并发布 VRFRequest 事件
- 数据请求发送时会附带WIN转账,作为使用费用
- 接受 WINkLink 节点提交的随机数和证明
- 将随机数发送至 Dapp 合约之前,VRFCoordinator 合约会对其证明进行验证
- 计算履行请求对应的 WINkLink 节点奖励
部署 VRFCoordinator 合约时,构造函数所需的参数如下:
constructor(
address wink,
address blockhashStore,
address winkMid
)
blockHashStore 为 BlockHashStore 地址;win WIN 为 WIN 代币地址;_winkMid 为 WinkMid 合约地址。
TIP
Nile 测试网
- WIN TRC20 合约地址:TNDSHKGBmgRx9mDYA9CnxPx55nu672yQw2
- WinkMid 合约地址:TFbci8j8Ja3hMLPsupsuYcUMsgXniG1TWb
- BlockHashStore 合约地址:TBpTbK9KQzagrN7eMKFr5QM2pgZf6FN7KA
- 测试网水龙头地址:https://nileex.io/join/getJoinPage (opens new window)
# VRFV2Wrapper 合约
VRFV2Wrapper 可简化交互,允许 Dapp 直接调用 VRFCoordinatorV2 合约。
配置参数
keyHash : 节点 keyhash
maxNumWords : 每个 VRF 请求包含的随机数个数上限,目前为 10
# 授权节点账户
节点账户需要授权才能向 VRFCoordinatorV2 合约提交数据,否则将报错。
VRFCoordinatorV2 合约的所有者需要调用以下合约,并将节点账户添加到白名单:
function registerProvingKey(address oracle, uint256[2] calldata publicProvingKey) external onlyOwner
oracle 为注册节点地址,用于接收支付的 WIN 代币 Dapp;publicProvingKey 为注册节点使用的公钥,用于生成随机数。
调用示例:
registerProvingKey(TYmwSFuFuiDZCtYsRFKCNr25byeqHH7Esb,['6273228386041830135141271310112248407537170435188969735053134748570771583756',67273502359025519559461602732298865784327759914690240925031700564257821594585'])
# Dapp 合约
设置 Consumer 合约的主要步骤如下:
- a) 导入并继承
VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// An example of a consumer contract that directly pays for each request.
pragma solidity ^0.8.7;
import "./VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase.sol";
contract VRFv2DirectFundingConsumer is VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase{}
- b) 合约必须执行 fulfillRandomWords 函数,该函数为 VRF 回调函数。 随机数返回合约后,添加处理逻辑。
function fulfillRandomWords(
uint256 _requestId,
uint256[] memory _randomWords
)
- c) 合约调用 requestRandomness 函数,触发 VRF 请求。
function requestRandomWords()
external
onlyOwner
returns (uint256 requestId)
{
requestId = requestRandomness(
msg.sender,
callbackGasLimit,
requestConfirmations,
numWords
);
s_requests[requestId] = RequestStatus({
paid: VRF_V2_WRAPPER.calculateRequestPrice(callbackGasLimit, numWords),
randomWords: new uint256[](0),
fulfilled: false
});
requestIds.push(requestId);
lastRequestId = requestId;
emit RequestSent(requestId, numWords);
return requestId;
}
# Dapp 合约示例
部署 sample consumer contract VRFv2DirectFundingConsumer.sol。
构造参数:
_winkAddress:Wink 代币合约地址
_winkMid: winkMid 合约地址
_wrapper:VRFV2Wrapper 合约地址
_numWords: 每个 vrf 请求的随机数个数上限
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// An example of a consumer contract that directly pays for each request.
pragma solidity ^0.8.7;
import "./ConfirmedOwner.sol";
import "./VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase.sol";
/**
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY.
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE.
* DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION.
*/
contract VRFv2DirectFundingConsumer is
VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase,
ConfirmedOwner
{
address winkAddress;
event RequestSent(uint256 requestId, uint32 numWords);
event RequestFulfilled(
uint256 requestId,
uint256[] randomWords,
uint256 payment
);
struct RequestStatus {
uint256 paid; // amount paid in wink
bool fulfilled; // whether the request has been successfully fulfilled
uint256[] randomWords;
}
mapping(uint256 => RequestStatus)
public s_requests; /* requestId --> requestStatus */
// past requests Id.
uint256[] public requestIds;
uint256 public lastRequestId;
// Depends on the number of requested values that you want sent to the
// fulfillRandomWords() function. Test and adjust
// this limit based on the network that you select, the size of the request,
// and the processing of the callback request in the fulfillRandomWords()
// function.
uint32 callbackGasLimit = 0;
// The default is 3, but you can set this higher.
uint16 requestConfirmations = 3;
// For this example, retrieve 2 random values in one request.
// Cannot exceed VRFV2Wrapper.getConfig().maxNumWords.
uint32 numWords;
constructor(
address _winkAddress,
address _winkMid,
address _wrapper,
uint32 _numWords
)
ConfirmedOwner(msg.sender)
VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase(_winkAddress, _winkMid, _wrapper) {
winkAddress = _winkAddress;
numWords = _numWords;
}
function requestRandomWords()
external
onlyOwner
returns (uint256 requestId)
{
requestId = requestRandomness(
callbackGasLimit,
requestConfirmations,
numWords
);
s_requests[requestId] = RequestStatus({
paid: VRF_V2_WRAPPER.calculateRequestPrice(callbackGasLimit, numWords),
randomWords: new uint256[](0),
fulfilled: false
});
requestIds.push(requestId);
lastRequestId = requestId;
emit RequestSent(requestId, numWords);
return requestId;
}
function fulfillRandomWords(
uint256 _requestId,
uint256[] memory _randomWords
) internal override {
require(s_requests[_requestId].paid > 0, "request not found");
s_requests[_requestId].fulfilled = true;
s_requests[_requestId].randomWords = _randomWords;
emit RequestFulfilled(
_requestId,
_randomWords,
s_requests[_requestId].paid
);
}
function getRequestStatus(
uint256 _requestId
)
external
view
returns (uint256 paid, bool fulfilled, uint256[] memory randomWords)
{
require(s_requests[_requestId].paid > 0, "request not found");
RequestStatus memory request = s_requests[_requestId];
return (request.paid, request.fulfilled, request.randomWords);
}
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./ConfirmedOwnerWithProposal.sol";
/**
* @title The ConfirmedOwner contract
* @notice A contract with helpers for basic contract ownership.
*/
contract ConfirmedOwner is ConfirmedOwnerWithProposal {
constructor(address newOwner) ConfirmedOwnerWithProposal(newOwner, address(0)) {}
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./OwnableInterface.sol";
/**
* @title The ConfirmedOwner contract
* @notice A contract with helpers for basic contract ownership.
*/
contract ConfirmedOwnerWithProposal is OwnableInterface {
address private s_owner;
address private s_pendingOwner;
event OwnershipTransferRequested(address indexed from, address indexed to);
event OwnershipTransferred(address indexed from, address indexed to);
constructor(address newOwner, address pendingOwner) {
require(newOwner != address(0), "Cannot set owner to zero");
s_owner = newOwner;
if (pendingOwner != address(0)) {
_transferOwnership(pendingOwner);
}
}
/**
* @notice Allows an owner to begin transferring ownership to a new address,
* pending.
*/
function transferOwnership(address to) public override onlyOwner {
_transferOwnership(to);
}
/**
* @notice Allows an ownership transfer to be completed by the recipient.
*/
function acceptOwnership() external override {
require(msg.sender == s_pendingOwner, "Must be proposed owner");
address oldOwner = s_owner;
s_owner = msg.sender;
s_pendingOwner = address(0);
emit OwnershipTransferred(oldOwner, msg.sender);
}
/**
* @notice Get the current owner
*/
function owner() public view override returns (address) {
return s_owner;
}
/**
* @notice validate, transfer ownership, and emit relevant events
*/
function _transferOwnership(address to) private {
require(to != msg.sender, "Cannot transfer to self");
s_pendingOwner = to;
emit OwnershipTransferRequested(s_owner, to);
}
/**
* @notice validate access
*/
function _validateOwnership() internal view {
require(msg.sender == s_owner, "Only callable by owner");
}
/**
* @notice Reverts if called by anyone other than the contract owner.
*/
modifier onlyOwner() {
_validateOwnership();
_;
}
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface OwnableInterface {
function owner() external returns (address);
function transferOwnership(address recipient) external;
function acceptOwnership() external;
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./TRC20Interface.sol";
import "./VRFV2WrapperInterface.sol";
/** *******************************************************************************
* @notice Interface for contracts using VRF randomness through the VRF V2 wrapper
* ********************************************************************************
* @dev PURPOSE
*
* @dev Create VRF V2 requests without the need for subscription management. Rather than creating
* @dev and funding a VRF V2 subscription, a user can use this wrapper to create one off requests,
* @dev paying up front rather than at fulfillment.
*
* @dev Since the price is determined using the gas price of the request transaction rather than
* @dev the fulfillment transaction, the wrapper charges an additional premium on callback gas
* @dev usage, in addition to some extra overhead costs associated with the VRFV2Wrapper contract.
* *****************************************************************************
* @dev USAGE
*
* @dev Calling contracts must inherit from VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase. The consumer must be funded
* @dev with enough WINK to make the request, otherwise requests will revert. To request randomness,
* @dev call the 'requestRandomness' function with the desired VRF parameters. This function handles
* @dev paying for the request based on the current pricing.
*
* @dev Consumers must implement the fullfillRandomWords function, which will be called during
* @dev fulfillment with the randomness result.
*/
abstract contract VRFV2WrapperConsumerBase {
TRC20Interface internal immutable WINK_TOKEN;
WinkMid internal immutable WINK_MID;
VRFV2WrapperInterface internal immutable VRF_V2_WRAPPER;
/**
* @param _winkMid is the address of WinkMid
* @param _vrfV2Wrapper is the address of the VRFV2Wrapper contract
*/
constructor(address _wink, address _winkMid, address _vrfV2Wrapper) {
WINK_TOKEN = TRC20Interface(_wink);
WINK_MID = WinkMid(_winkMid);
VRF_V2_WRAPPER = VRFV2WrapperInterface(_vrfV2Wrapper);
}
/**
* @dev Requests randomness from the VRF V2 wrapper.
*
* @param _callbackGasLimit is the gas limit that should be used when calling the consumer's
* fulfillRandomWords function.
* @param _requestConfirmations is the number of confirmations to wait before fulfilling the
* request. A higher number of confirmations increases security by reducing the likelihood
* that a chain re-org changes a published randomness outcome.
* @param _numWords is the number of random words to request.
*
* @return requestId is the VRF V2 request ID of the newly created randomness request.
*/
function requestRandomness(
uint32 _callbackGasLimit,
uint16 _requestConfirmations,
uint32 _numWords
) internal returns (uint256 requestId) {
uint64 amount = VRF_V2_WRAPPER.calculateRequestPrice(_callbackGasLimit, _numWords);
WINK_TOKEN.approve(address(WINK_MID), amount);
WINK_MID.transferAndCall(
address(VRF_V2_WRAPPER),
amount,
abi.encode(_callbackGasLimit, _requestConfirmations, _numWords)
);
return VRF_V2_WRAPPER.lastRequestId();
}
/**
* @notice fulfillRandomWords handles the VRF V2 wrapper response. The consuming contract must
* @notice implement it.
*
* @param _requestId is the VRF V2 request ID.
* @param _randomWords is the randomness result.
*/
function fulfillRandomWords(uint256 _requestId, uint256[] memory _randomWords) internal virtual;
function rawFulfillRandomWords(uint256 _requestId, uint256[] memory _randomWords) external {
require(msg.sender == address(VRF_V2_WRAPPER), "only VRF V2 wrapper can fulfill");
fulfillRandomWords(_requestId, _randomWords);
}
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface VRFV2WrapperInterface {
/**
* @return the request ID of the most recent VRF V2 request made by this wrapper. This should only
* be relied option within the same transaction that the request was made.
*/
function lastRequestId() external view returns (uint256);
/**
* @notice Calculates the price of a VRF request with the given callbackGasLimit at the current
* @notice block.
*
* @dev This function relies on the transaction gas price which is not automatically set during
* @dev simulation. To estimate the price at a specific gas price, use the estimatePrice function.
*
* @param _callbackGasLimit is the gas limit used to estimate the price.
*/
function calculateRequestPrice(uint32 _callbackGasLimit, uint32 _numWords) external view returns (uint64);
// /**
// * @notice Estimates the price of a VRF request with a specific gas limit and gas price.
// *
// * @dev This is a convenience function that can be called in simulation to better understand
// * @dev pricing.
// *
// * @param _callbackGasLimit is the gas limit used to estimate the price.
// * @param _requestGasPriceWei is the gas price in wei used for the estimation.
// */
// function estimateRequestPrice(uint32 _callbackGasLimit, uint256 _requestGasPriceWei) external view returns (uint256);
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
abstract contract TRC20Interface {
function totalSupply() public view virtual returns (uint);
function balanceOf(address guy) public view virtual returns (uint);
function allowance(address src, address guy) public view virtual returns (uint);
function approve(address guy, uint wad) public virtual returns (bool);
function transfer(address dst, uint wad) public virtual returns (bool);
function transferFrom(address src, address dst, uint wad) public virtual returns (bool);
event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
}
abstract contract WinkMid {
function setToken(address tokenAddress) public virtual;
function transferAndCall(address to, uint64 tokens, bytes calldata _data) public virtual returns (bool success);
function balanceOf(address guy) public view virtual returns (uint);
function allowance(address src, address guy) public view virtual returns (uint);
}
# 如何设置可验证随机函数合约
# WinkMid 合约
WINkLink 用 WIN 代币(TRC20)作为整个生态的基础代币。
WINkLink 使用了 transferAndCall 功能,即在转账 TRC20 代币给合约的同时调用合约的某一回调函数,该功能类似 ERC677,但接口参数不同。
考虑到绝大多数已发行的代币无法再修改合约或增加接口,WINkLink 提供 WinkMid 包装合约,可用来包装任一 TRC20 代币,并提供 transferAndCall 接口。
合约代码可于 WinkMid.sol 查看。
为方便开发者使用,Nile 测试网部署了 WinkMid 合约,并封装了 WIN 代币。 开发者可直接使用该合约地址,无需额外部署。 Nile 测试网还提供水龙头地址,用户可以领取 TRX 和 WIN 测试代币。
TIP
Nile 测试网
WIN TRC20 合约地址: TNDSHKGBmgRx9mDYA9CnxPx55nu672yQw2
WinkMid 合约地址: TJpkay8rJXUWhvS2uL5AmMwFspQdHCX1rw
测试网水龙头地址: https://nileex.io/join/getJoinPage (opens new window)
部署 WinkMid 合约时,开发者需在构造函数中提供被封装的 TRC20 代币地址(即 WIN 代币地址)。
WinkMid 合约可帮助用户进行合约调用,开发者无需直接进行调用操作。
部署 Coordinator 合约时需在构造函数中提供 WIN 代币地址和 WinkMid 合约地址。
# VRFCoordinatorV2
Coordinator 主要负责处理所有 VRF 请求和 fulfillment, 请使用相应的参数部署合约。
发起请求之前,预言机必须以 base58 编码的形式用证明密钥向 Coordinator 注册其节点地址,否则请求将失败。
# VRFV2Wrapper
Wrapper 合约是直接付费 Consumer 的访问层。该合约通过 WinkMid 的 transferAndCall 函数为订阅服务提供充足的 Wink 代币,保证内部流通。
传入数据为 ABI 编码格式的订阅 ID 值,例如,0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007 表示订阅 ID 为 7。
TIP
keyhash 指的是预言机节点的 keyhash,可通过 Operator UI 或 CLI 获取
# Consumers
- VRFv2DirectFundingConsumer
在发起请求时,直接付费的 Consumer 会直接从用户账户中扣除 Wink 代币。 请求时,该 Consumer 接口会与 Wrapper 合约进行交互。
- VRFv2SubscriptionConsumer
为确保订阅服务处于开启状态,订阅服务 Consumer 需要使用订阅服务管理器。 出现请求时,该 Consumer 接口凭有效的订阅 ID 直接与 Coordinator 合约进行交互。
WARNING
代码中提供的 Consumer 合约仅作示例,用户应根据自身情况编写自己的 Consumer 合约。
# 为节点添加 VRF 任务
以下是创建一个所需最少参数的 VRF 任务规范示例模版
type = "vrf"
schemaVersion = 1
name = "vrf-delete-test"
forwardingAllowed = false
coordinatorAddress = "THE-SMART-CONTRACT-EIP55-COORDINATOR-ADDRESS"
fromAddresses = [ "THE-CURRENT-NODE-EIP55-ADDRESS" ]
minIncomingConfirmations = 1
publicKey = "THE-CURRENT-NODE-PUBLIC-KEY"
observationSource = """
decode [type="tvmabidecodelog"]
vrf [type=vrfbuilder]
tvmcall [type=tvmcall contract="THE-SMART-CONTRACT-TRON-ADDRESS" extractRevertReason=true]
decode->vrf->tvmcall
"""
创建完成后,节点便可以处理收到的 VRF 请求。